In today’s interconnected world, food systems are more than just a complex network of activities and processes. They are the lifeblood that ensures we have enough food to eat, that it’s nutritious, and that our planet can sustainably support us. These systems encompass everything from planting seeds in the ground to enjoying a meal with loved ones. It’s important for us to understand the different components and challenges of food systems so that we can tackle global issues like climate change and environmental degradation.
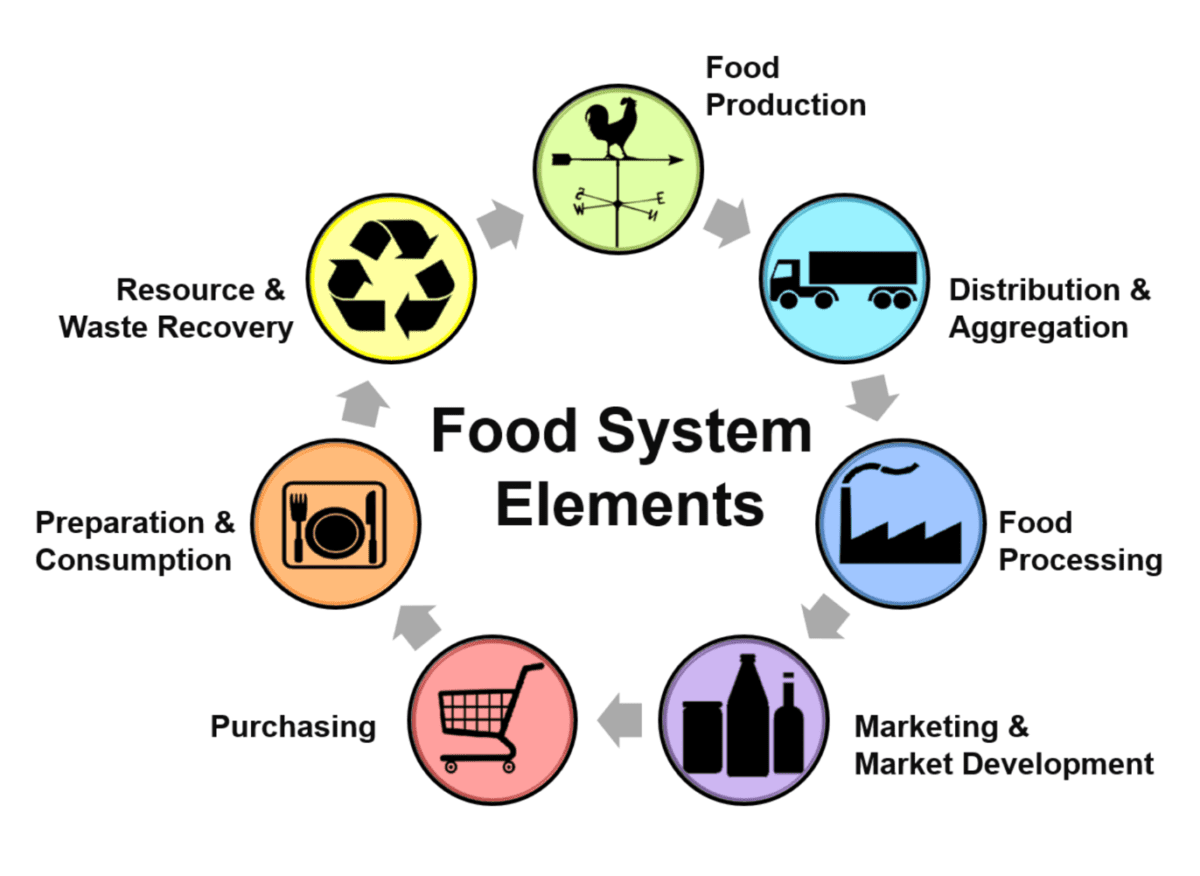
At the heart of any food system lies the production phase, where farmers cultivate crops, raise livestock, and harvest fish or seafood. It’s here that sustainable practices become crucial. Taking care of the soil, using water efficiently, and controlling pests in natural ways are all vital to minimize our impact on the environment and preserve our precious resources.
Once food is harvested, it goes through processing and manufacturing stages to transform it into various products. These processes, such as cleaning, sorting, cooking, and packaging, not only make our food safer and last longer but also add value to the products. Efficient food processing facilities are essential to maintain the quality of our food throughout the supply chain.
After processing, comes the distribution and logistics phase, where food is transported and delivered to markets, stores, restaurants, and institutions. A well-designed network of transportation systems, including trucks, ships, planes, and railways, helps us reduce waste and ensure that food reaches its destination on time. Effective management of logistics improves the efficiency of the entire food system.
Then, it’s up to retail outlets like supermarkets, farmers’ markets, and restaurants to make sure that food meets the needs of consumers. What we choose to buy and eat greatly influences the demand for different types of food products and shapes the overall food system. By promoting healthy and sustainable choices, we can create a resilient and nutritious food system for everyone.
Food waste and loss are significant challenges we face in our food systems. Proper management of food waste, such as recycling and composting, is vital to protect our environment and conserve resources. Minimizing food waste not only helps us use our resources wisely but also reduces greenhouse gas emissions.
Governments, international organizations, and regulatory bodies play a crucial role in shaping our food systems through policies, regulations, and incentives. Their actions support sustainable production methods, ensure food safety standards, and address social and economic issues related to food access and affordability. Strong policy frameworks and effective governance are essential for building resilient and equitable food systems.
Socioeconomic and cultural factors also influence our food systems. Dietary preferences, traditions, and food-related behaviors vary across different communities and impact food availability, accessibility, and affordability. It’s important for us to address these factors and create inclusive and equitable food systems that prioritize food security and improved livelihoods for all.
The concept of food systems has gained increasing attention as we face global challenges like population growth, climate change, and environmental degradation. The United Nations recognizes the importance of food systems in achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly SDG 2, which focuses on ending hunger, achieving food security, improving nutrition, and promoting sustainable agriculture.
To build sustainable food systems, we need to adopt environmentally friendly and resource-efficient agricultural practices. This includes methods like organic farming, agroecology, precision agriculture, and conservation agriculture, which minimize the use of chemicals, protect soil health, conserve water, and promote biodiversity. These practices not only reduce the environmental impact but also contribute to long-term food security by preserving natural resources and making our food system more resilient to climate change.
Reducing food loss and waste is another important aspect of building a resilient food system. Approximately one-third of the food produced globally is lost or wasted, leading to significant economic, social, and environmental consequences. We can address this issue by improving post-harvest handling, and implementing better storage and transportation infrastructure. Enhanced packaging and labeling can also help in reducing food waste. Furthermore, educating consumers and raising awareness about the impact of food waste can encourage responsible consumption habits.
Inclusivity and equity are vital considerations when it comes to our food systems. Access to nutritious and affordable food is a fundamental right that should be available to all individuals. Unfortunately, hunger and malnutrition still plague millions of people worldwide. To achieve true food security, we must not only increase food production but also address underlying issues such as poverty, gender inequality, and inadequate infrastructure. Empowering small-scale farmers and marginalized communities through improved access to land, credit, markets, and agricultural technologies can make a significant difference. By doing so, we can create more equitable food systems that uplift livelihoods and ensure that everyone has access to the nourishment they need.
In the face of global challenges, building sustainable and resilient food systems has become imperative. By adopting environmentally friendly agricultural practices, reducing food loss and waste, and promoting inclusivity and equity, we can pave the way for a future where food security, nutrition, and sustainable development are achievable for all. The United Nations’ recognition of food systems as a key driver in achieving the Sustainable Development Goals highlights the urgency for us to transform our current practices and create food systems that not only nourish people but also protect our planet. It is a collective effort that requires us to work together, hand in hand, to shape a brighter future through resilient and sustainable food systems.
Subscribe to our YouTube Channel and watch other insightful agricultural and entertaining videos.